Team:Beijing HDFLS High/Project
From 2014hs.igem.org
(→Step) |
(→RESULTS AND CONCLUSION) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[File:Bees3.png|mid|600px]] | [[File:Bees3.png|mid|600px]] | ||
| - | =RESULTS AND | + | =RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS= |
==Step== | ==Step== | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 8 June 2014
Contents |
TITLE
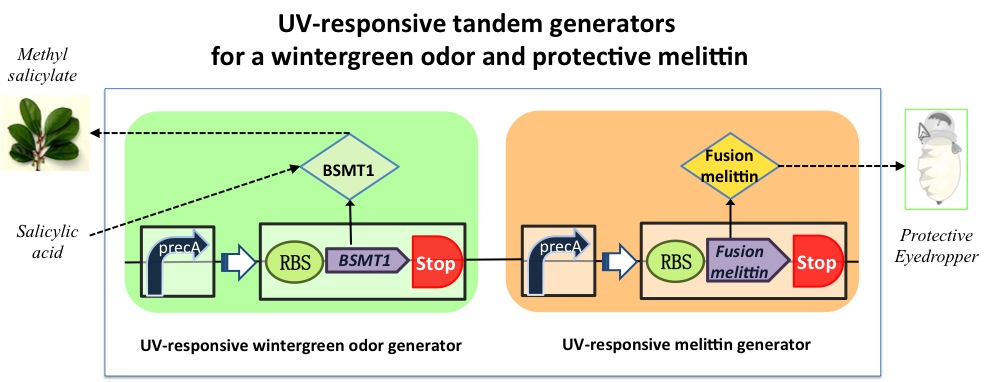
The UV-responsing generators for a wintergreen odor and protective melittin
ABSTRACT
We design a bacteria that produces a wintergreen odor and protective melittin under extensive UV radiation. The biological system includes two generators: the UV-responsing wintergreen odor generator (BBa_K994000) and UV-responsing melittin generator. The melittin generator is composed of two transcriptional devices: RecA (SOS) promoter (BBa_J22106) and synthesized melittin gene with enterokinase digested sequence. The protective generator takes as input extensive UV radiation and produces as output fusion melittin. Melittin can improve immunity and scavenging free radicals to alleviate the harm from electromagnetic radiation, such as UV and blue light.
BACKGROUD
As the students in an international school, we always face many different kinds of assessment events and each of them need to finished by computer. After using Internet whole day, our eyes would feel uncomfortable with innumerable distinct kind radiations. How can we deal with it?
The eye is a complex organ, composed of many different structures with varying sensitivity to the effects of radiation. An easy way to look at the eye is to divide it into zones that can be examined with respect to their susceptibility to radiation effects. It is also noteworthy that the effects of radiation on the eye not only depend on the sensitivity of the tissue itself but also on the mode of radiation delivery.

RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Step
Step1
We have to got Part A and Part B's DNA before we digestion. Part A will be used after transformation and miniprep. We got Part B by artificial synthesis.
Step2
Digestion
Step3
Electrophoresis
Step4
Ligation
Step5
Sequencing
 "
"
