Team:Beijing HDFLS High/Project
From 2014hs.igem.org
Contents |
TITLE
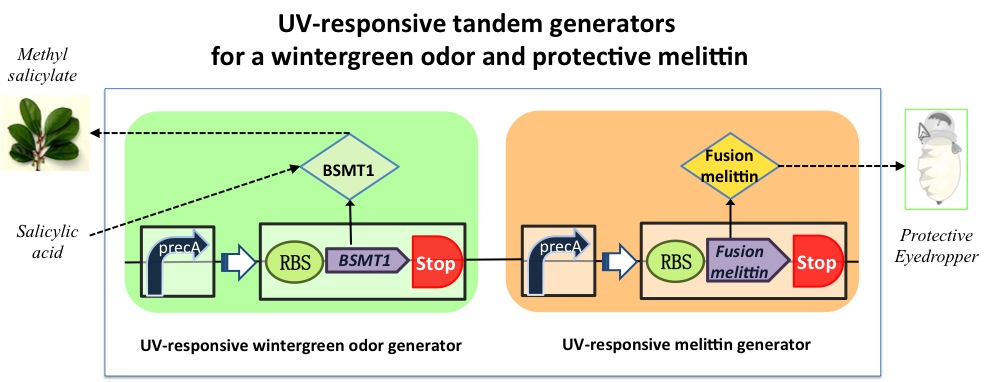
The UV-responsing tandem generators for a wintergreen odor and protective melittin
ABSTRACT
We design a bacteria that produces a wintergreen odor and protective melittin under extensive UV radiation. The biological system includes two generators: the UV-responsing wintergreen odor generator (BBa_K994000) and UV-responsing melittin generator. The melittin generator is composed of two transcriptional devices: RecA (SOS) promoter (BBa_J22106) and synthesized melittin gene with enterokinase digested sequence. The protective generator takes as input extensive UV radiation and produces as output fusion melittin. Melittin can improve immunity and scavenging free radicals to alleviate the harm from electromagnetic radiation, such as UV and blue light.
BACKGROUD
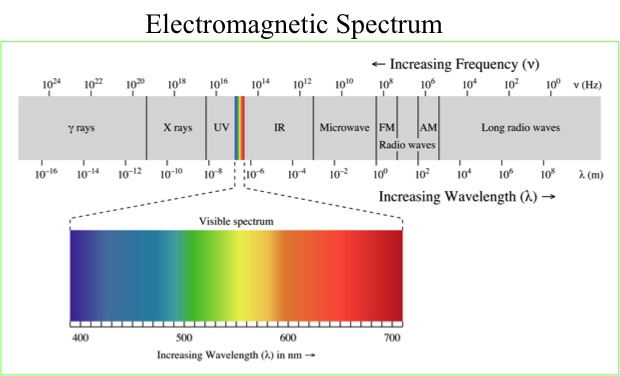
The electromagnetic spectrum, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength, can be divided, for practical engineering purposes, into radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. The eyes of various organisms sense a relatively small range of frequencies of EMR called the visible spectrum or light. Higher frequencies (shorter wavelengths) correspond to proportionately more energy carried by each photon. Blue light is the most energetic portion of the visible light spectrum, it's less energetic than UV radiation but it also has the ability to penetrate into tissue and cause cellular damage.
Blue light is the hardest for the eye to focus on. We actually see a halo around bright blue light. Blue light scatters more inside the eyeball than other colors, producing more glare, more eyestrain and more fatigue. Intense blue light can cause damage to the retina, because blue is the hardest color for the retina to handle.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Step
Step1
We have to got Part A and Part B's DNA before we digestion. Part A will be used after transformation and miniprep. We got Part B by artificial synthesis.
Step2
Digestion
Step3
Electrophoresis
Step4
Ligation
Step5
Sequencing
 "
"